In the realm of physics and engineering, understanding the concepts of frequency, wavelength, and period is crucial. These fundamental properties describe various aspects of waves, from sound waves to electromagnetic radiation. This article aims to delve into the definitions of frequency, wavelength, and period, as well as explore their interrelationships.
Frequency Definition:
Frequency refers to the number of occurrences of a repeating event per unit of time. In the context of waves, it represents how many cycles of a wave occur in one second. The standard unit of frequency is hertz (Hz), where 1 Hz equals one cycle per second. Higher frequencies correspond to more cycles occurring in the same amount of time, while lower frequencies signify fewer cycles.
Mathematically, frequency (f) is calculated using the formula:

Wavelength Definition:
Wavelength, denoted by the symbol λ (lambda), is the distance between two successive crests or troughs of a wave. It represents the spatial extent of one cycle of the wave. Wavelength is typically measured in meters (m) or its multiples, such as nanometers (nm) for electromagnetic waves.
In mathematical terms, the relationship between wavelength, frequency, and the speed of the wave (v) is given by the formula:

Period Definition:
Period (T) is the time taken for one complete cycle of a wave to pass a given point. It is the reciprocal of frequency and represents the inverse of how frequently the wave repeats itself. Period is measured in seconds (s).
The mathematical relationship between period and frequency is given by:

Relationships Between Frequency, Wavelength, and Period:
Frequency, wavelength, and period are intimately related through the properties of waves. The following relationships summarise their connections:
Frequency and Wavelength:
- As frequency increases, wavelength decreases, and vice versa. This relationship is inversely proportional.
- Higher frequency waves have shorter wavelengths, while lower frequency waves have longer wavelengths.
- This relationship is described by the equation
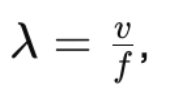
where v is the speed of the wave, which remains constant for a given medium.
Frequency and Period:
- Frequency and period are inversely related. As frequency increases, the period decreases, and vice versa.
- This relationship is described by the equation
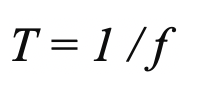
- Higher frequency waves have shorter periods, meaning they repeat more frequently in a given time interval, while lower frequency waves have longer periods.
Conclusion:
Frequency, wavelength, and period are fundamental properties that describe different aspects of waves. Frequency represents the rate of wave oscillations per unit of time, while wavelength signifies the spatial extent of one cycle of the wave. Period, on the other hand, represents the time taken for one complete cycle to occur. These properties are interconnected through mathematical relationships, allowing scientists and engineers to analyse and understand various wave phenomena across different disciplines. Understanding these concepts is essential for fields such as acoustics, optics, telecommunications, and beyond.