Laser, an acronym for Light Amplification by Stimulated Emission of Radiation, has become an indispensable technology with diverse applications across various fields. Originally developed in the mid-20th century, lasers have evolved into a versatile tool with numerous applications that have significantly impacted science, industry, medicine, communication, and entertainment.
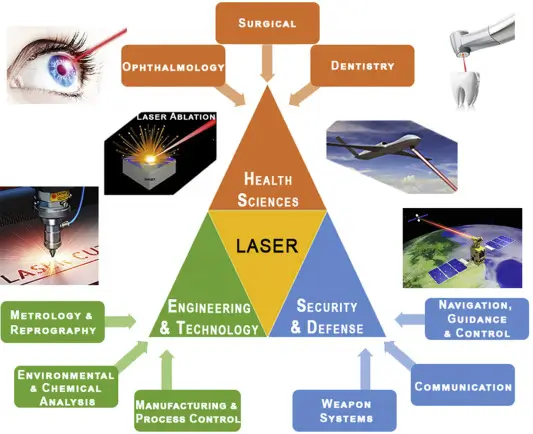
1. Communication:
Fiber Optic Communication: Lasers are widely used in fiber optics to transmit data over long distances. The coherent and monochromatic nature of laser light ensures high-speed and reliable communication, facilitating the backbone of the internet and telecommunications networks.
2. Industrial Applications:
Cutting and Welding: High-powered lasers are employed in manufacturing for cutting and welding metals and other materials. This precise and efficient method has become a standard in industries like automotive, aerospace, and electronics.
Laser Marking and Engraving: Lasers are used for marking and engraving on various materials, providing a permanent and precise solution for product identification and decoration.
3. Medical Applications:
Surgery: Lasers have revolutionised surgery by offering minimally invasive procedures with reduced bleeding and faster recovery times. They are used in eye surgeries (LASIK), dermatology, dentistry, and even cancer treatments.
Medical Imaging: Lasers play a crucial role in medical imaging techniques such as laser-induced fluorescence, confocal microscopy, and optical coherence tomography (OCT).
4. Scientific Research:
Spectroscopy: Lasers are essential tools in spectroscopic analysis, helping researchers study the composition and structure of materials. They enable precise measurements and analysis in fields like chemistry, physics, and environmental science.
Laser Cooling and Trapping: In atomic physics, lasers are used to cool and trap atoms, allowing scientists to study fundamental quantum phenomena and develop atomic clocks with unprecedented accuracy.
5. Entertainment:
Laser Light Shows: Lasers are a key element in creating mesmerising light shows for entertainment purposes. They are used in concerts, laser displays, and theme park attractions to produce vibrant and dynamic visual effects.
6. Defence and Security:
Lidar Technology: Laser-based radar, known as Lidar, is used for range finding, mapping, and object detection. It is a crucial technology in autonomous vehicles and has applications in military surveillance and reconnaissance.
Directed Energy Weapons: Lasers are explored as potential components in directed energy weapons for defence applications, offering precision and speed in targeting.
7. Environmental Monitoring:
Remote Sensing: Lasers play a crucial role in remote sensing technologies, such as Light Detection and Ranging (LIDAR), which is used for mapping terrain, monitoring forests, and studying atmospheric composition.
Conclusion:
The applications of laser technology are vast and continue to expand as researchers and engineers discover new ways to harness the unique properties of laser light. From enabling high-speed communication to revolutionising medical procedures and contributing to scientific advancements, lasers have become an integral part of our modern technological landscape, illuminating the way for progress in various fields.