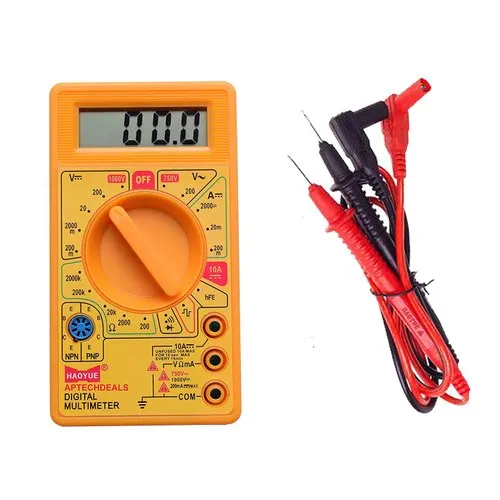
In the realm of electronics and electrical engineering, precision measurement is paramount. One indispensable tool that plays a pivotal role in this domain is the Digital Multimeter (DMM). This versatile device has become a staple in both professional and hobbyist toolkits, offering a myriad of functions to measure, test, and troubleshoot electrical circuits. In this article, we delve into the intricacies of digital multimeters, exploring their features, applications, and how to use them effectively.

I. Understanding Digital Multimeters:
Overview:
A Digital Multimeter, often abbreviated as DMM, is a portable electronic instrument used for measuring multiple electrical parameters such as voltage, current, resistance, capacitance, and continuity. Unlike its analog predecessor, digital multimeters provide precise readings on a digital display, offering improved accuracy and ease of use.
Components:
- Display: The digital readout where measurement values are displayed.
- Function Selection Dial: Allows users to choose the desired measurement function (e.g., voltage, current, resistance).
- Input Terminals: Connect probes or leads to measure electrical parameters.
- Mode Buttons: Enable additional measurement functions like frequency, capacitance, and temperature.
- Range Selector: Adjusts the sensitivity of the measurement range.
II. Applications of Digital Multimeters:
1. Voltage Measurement :
DC Voltage : Used to measure the direct current voltage in a circuit.
AC Voltage : Measures the alternating current voltage, commonly used for household electrical systems.
2. Current Measurement:
DC Current : Measures the flow of direct current in a circuit.
AC Current : Measures the alternating current flow.
3. Resistance Measurement : Determines the resistance in ohms of a resistor or component in a circuit.
4. Continuity Testing : Verifies the existence of a complete path in a circuit, usually with an audible beep for a low-resistance connection.
5. Capacitance Measurement : Measures the capacitance of capacitors in a circuit.
6. Frequency Measurement : Measures the frequency of an AC signal.
7. Temperature Measurement : Some advanced digital multimeters come equipped with temperature probes for measuring temperature in Celsius or Fahrenheit.
III. How to Use a Digital Multimeter:
1. Safety Precautions:
Ensure the equipment is turned off before making measurements.
Use the appropriate measurement range to avoid damage.
Verify the multimeter’s functionality by testing known voltage sources.
2. Basic Measurement Procedure:
- Set the function dial to the desired measurement parameter (voltage, current, resistance).
- Connect the multimeter probes to the circuit or component being measured.
- Select the appropriate range for accurate readings.
- Read the measurement value on the digital display.
3. Troubleshooting:
- Use continuity testing to identify open or short circuits.
- Measure voltages and currents to identify irregularities.
- Check resistance values to ensure proper component functionality.
Conclusion:
Digital Multimeters have revolutionised the field of electronics by providing accurate and versatile measurement capabilities. Whether you are an electronics professional, hobbyist, or student, understanding the features, applications, and proper usage of a digital multimeter is essential for efficient circuit analysis, troubleshooting, and maintenance. As technology continues to advance, these indispensable tools will remain at the forefront of electrical measurement and diagnostics, ensuring the integrity and reliability of electronic systems worldwide.