Understanding Gas Laws: A Comprehensive Overview
Gases are one of the fundamental states of matter, and their behaviour can be described by a set of laws known as gas laws. These laws relate various properties of gases, such as pressure, volume, temperature, and the number of moles. The study of gas laws is crucial in understanding and predicting the behaviour of gases under different conditions. In this article, we will explore four fundamental gas laws: Boyle’s Law, Charles’s Law, Avogadro’s Law, and the Ideal Gas Law.
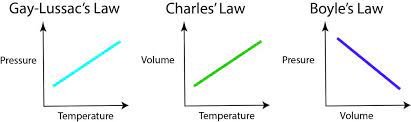
1. Boyle's Law:
Boyle’s Law describes the relationship between the pressure and volume of a gas at constant temperature. It states that the pressure of a given amount of gas is inversely proportional to its volume. Mathematically, it can be expressed as:

This law implies that if the volume of a gas decreases, its pressure increases, and vice versa, as long as the temperature remains constant.
2. Charle's Law
Charles’s Law describes the relationship between the volume and temperature of a gas at constant pressure. It states that the volume of a given amount of gas is directly proportional to its absolute temperature. Mathematically, it can be expressed as:
Charles’s Law implies that as the temperature of a gas increases, its volume also increases, provided that the pressure remains constant.
3. Avogadro's Law:
Avogadro’s Law describes the relationship between the volume and the amount of gas at constant temperature and pressure. It states that the volume of a gas is directly proportional to the number of moles of the gas. Mathematically, it can be expressed as:

Avogadro’s Law implies that equal volumes of gases, at the same temperature and pressure, contain an equal number of moles.
4. Ideal Gas Law:
The Ideal Gas Law combines Boyle’s, Charles’s, and Avogadro’s laws into a single equation that relates the pressure, volume, temperature, and amount of gas. The Ideal Gas Law is given by:
PV=nRT
Where,
P is the pressure of the gas.
V is the volume of the gas.
n is the number of moles of the gas.
R is the ideal gas constant.
T is the temperature of the gas in Kelvin.
The Ideal Gas Law is applicable under conditions where the gas behaves ideally, meaning the gas particles have negligible volume and no intermolecular forces.
Conclusion:
In conclusion, understanding gas laws is essential for predicting and manipulating the behaviour of gases in various situations. These laws provide a foundation for the study of thermodynamics and are crucial in fields such as chemistry, physics, and engineering. Whether analysing the expansion of a gas in a balloon or calculating the pressure changes in a chemical reaction, gas laws play a central role in describing the physical properties of gases.