The Milky Way Galaxy, a celestial masterpiece spanning across vast expanses of space, has captured the imagination of humanity for centuries. Its name originates from its appearance as a milky band of light stretching across the night sky, a sight that has inspired wonder and contemplation among countless generations. In this article, we embark on a journey through the Milky Way, exploring its structure, composition, and the awe-inspiring phenomena that populate its reaches.
Formation and Structure:
The Milky Way Galaxy formed approximately 13.6 billion years ago, emerging from the gravitational collapse of a vast cloud of gas and dust. Over eons, this primordial material coalesced into the intricate structure we observe today. At its core lies a dense region known as the galactic bulge, teeming with old stars and a supermassive black hole, named Sagittarius A*, which holds sway over the galactic centre.
Radiating outward from the bulge are the luminous spiral arms, adorned with countless stars, interstellar gas, and dust. These arms, comprised primarily of hydrogen gas and dust, serve as the cradles for stellar nurseries, where new stars are born amidst the swirling clouds of gas and dust.
Stellar Population:
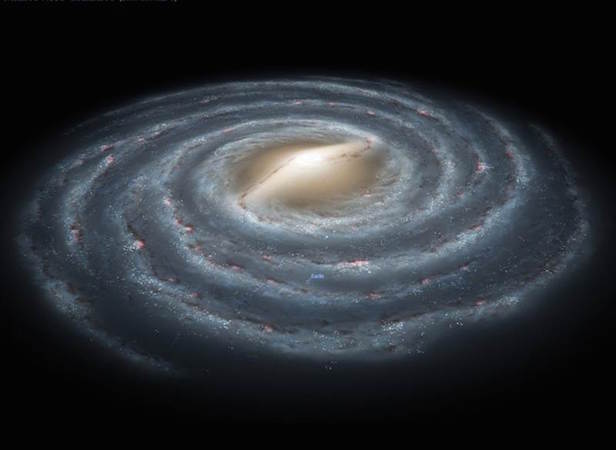

The Milky Way is home to a staggering array of stars, ranging from massive, luminous giants to diminutive, faint dwarfs. Our Sun, a middle-aged star nestled within one of the galaxy’s spiral arms, is but one of an estimated 100 billion stars that populate the Milky Way. These stars come in a variety of spectral types, colours, and sizes, each contributing to the tapestry of light that defines our galactic home.
Interstellar Medium:
Interspersed among the stars is the interstellar medium, a diffuse mixture of gas and dust that pervades the galaxy. This medium serves as the raw material for star formation and plays a crucial role in the lifecycle of stars. Within the interstellar medium, complex molecules form, giving rise to the building blocks of life and offering tantalising clues to the origins of life in the universe.
Galactic Dynamics:
The Milky Way is in a constant state of motion, with stars orbiting the galactic centre at varying speeds. Our solar system, located approximately 26,000 light-years from the galactic centre, completes a full orbit roughly every 230 million years. This dynamic motion shapes the structure of the galaxy, sculpting its spiral arms and influencing the distribution of stars and gas.
Galactic Halo and Dark Matter:

Surrounding the luminous disk of the Milky Way is a vast halo of dark matter, an enigmatic substance that comprises the majority of the galaxy’s mass. Dark matter, though invisible and undetectable through conventional means, exerts a gravitational influence that binds the galaxy together and contributes to the stability of its structure. Despite its elusive nature, dark matter remains a central focus of astronomical research, offering insights into the fundamental nature of the cosmos.
Galactic Phenomena:
The Milky Way is a stage upon which a myriad of cosmic phenomena unfold. From dazzling nebulae and star clusters to cataclysmic supernovae and enigmatic black holes, the galaxy teems with activity and intrigue. Nebulae, vast clouds of gas and dust, serve as the birthplaces of stars and showcase the spectacular beauty of cosmic creation. Star clusters, both young and old, dot the galactic landscape, each a testament to the dynamic processes that shape the evolution of stars.
Conclusion:
In the vast expanse of the cosmos, the Milky Way Galaxy stands as a testament to the grandeur and complexity of the universe. From its humble origins to its majestic spiral arms, our galactic home inspires awe and curiosity, inviting us to explore its mysteries and unravel the secrets of the cosmos. As we gaze upon the luminous band of light that stretches across the night sky, we are reminded of our place within the vast tapestry of the universe, humbled by the boundless beauty and wonder that surrounds us.